Java Script(Prototype / 표준 내장 객체의 확장 / Object)
Prototype / 표준 내장 객체의 확장
Prototype
function Ultra(){}
Ultra.prototype.ultraProp = true;
function Super(){}
Super.prototype = new Ultra();
function Sub(){}
Sub.prototype = new Super();
var o = new Sub();
console.log(o.ultraProp);
Ultra.protype에 담겨져 있는 프로퍼티(속성)은 ultraProp = true; 이 담겨져있고,
Super.protoypype에 Ultra객체가 담겨져있으며, Sub.prototype에는 Super객체가 담겨져있다.
이러한 현상을 Prototype Chain 이라고한다. 때문에 결과적으로 true가 나오게된다.
- prototype에 저장된 속성들은 생성자를 통해서 객체를 만들어질 때 그 객체에 연결된다.
function Ultra(){}
Ultra.prototype.ultraProp = true;
function Super(){}
var t = new Ultra();
Super.prototype = t;
function Sub(){}
var s = new Super();
s.ultraProp = 3;
Sub.prototype = s;
var o = new Sub();
console.log(o.ultraProp);
var o에는 ultraProp 라는 프로퍼티가 없다. 자바스크립트는 o의 prototype을 찾는다
찾았더니 sub.prototype에 저장되어있는 객체인 new Super에 3이라는 값이 저장되어있기 때문에 3이라는 결과가 나온다.
표준 내장 객체의 확장
표준 내장 객체는 자바스크립트가 기본적으로 가지고 있는 객체들을 의미한다. 내장 객체가 중요한 이유는 프로그래밍을 하는데 기본적으로 필요한 도구이기 때문이다.
- 자바스크립트의 내장 객체
- Obejct
- Function
- Array
- String
- Boolean
- Number
- Math
- Date
- ReqExp
배열의 확장
var arr = new Array('Seoul','new york', 'ladarkh','pusan','Tsukuba');
function getRandomValueFromArray(arr){
var index = Math.floor(arr.length*Math.random());
return arr[index];
}
console.log(getRandomValueFromArray(arr));
Array는 배열을 생성할때 사용하는 전역객체이다.
위 예제는 메소드를 이용하여 배열의 항목들을 랜덤적으로 나오게하는 예제이다.
arr.length로 인덱스의 길이를, Math.random()으로 0.1~0.9까지의 랜덤숫자가 나오도록 만들고,
Math.floor로 소수점뒤의 자리를 버리게 만들면 0~4까지의 숫자가 나오게된다.
Array.prototype.random = function(){
var index = Math.floor(this.length*Math.random());
return this[index];
}
var arr = new Array('Seoul','new york', 'ladarkh','pusan','Tsukuba');
console.log(arr.random());
위 예제도 같은 결과가 나오는 예제이지만, protype으로 Array객체에 접근하여 random프로퍼티를 추가한 예제이다. 이렇게 하면 매개변수를 사용할 필요없이 바로 사용이 가능하다는 장점이 있다.
Object
Object는 모든 객체의 상위 즉, 모든 객체는 Object를 상속하고 있다.
그런 이유로 모든 객체는 Object 객체의 프로퍼티를 가지고 있다. 또한 Object 객체를 확장하면 모든 객체가 접근할 수 있는 API를 만들 수 있다.
Object.prototype.contain = function(needle){
for(var name in this){
if(this[name] === needle){
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
var o = {'name':'egoing','city':'seoul'}
console.log(o.contain('egoing'));
var a = ['egoing','leezche','grapittie'];
console.log(a.contain('leezche'));
위 예제처럼 Object.prototype으로 contain프로퍼티를 만들어서 사용하면
모든 객체들은 contain을 사용할 수 있게된다.
하지만 모든 객체에 영향을 주기 때문에 위험하다.
for (var name in o){
console.log(name);
}
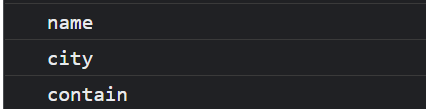
contain이라는 객체에 없는 속성값이 나오게된다.
댓글남기기